Chapter 4 Seasonal Anomaly Modeling
Seasonal zooplankton anomalies are estimated for each taxa and life-stage group independently based on their intra-annual patterns in abundance. For this estimation, a generalized additive model (GAM) is used to model log(abundance) throughout the year using the Julian day (day of year, 1-365) as the independent variable or predictor of the log(abundance). The model we fit uses a cubic cyclic spline smoother: bs = "cc" which specifies a cyclic cubic regression spline (see cyclic.cubic.spline). i.e. a penalized cubic regression splines whose ends match, up to second derivative.
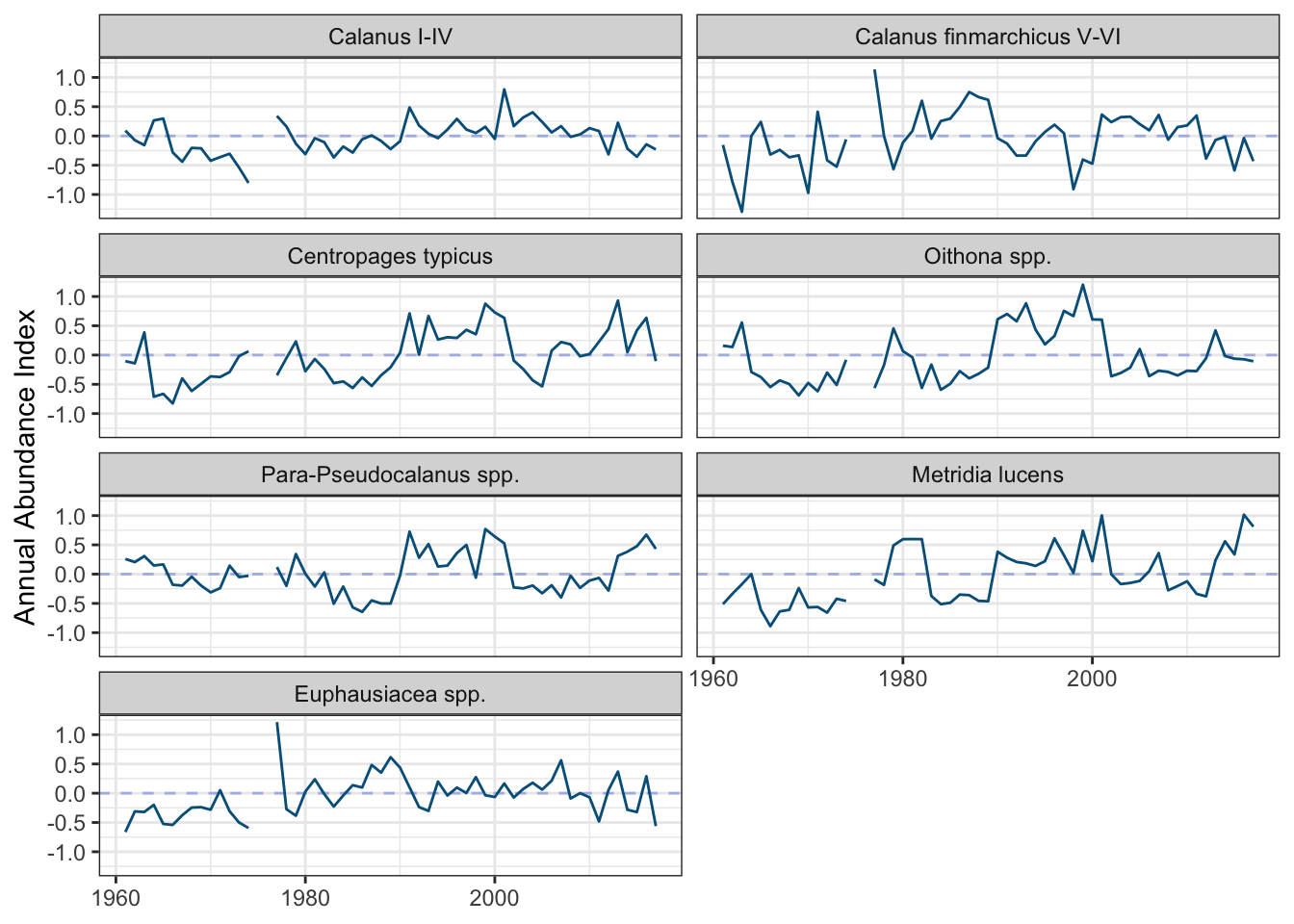
If we take the observed abundances and subtract out the predicted seasonal abundance we are left with seasonal anomalies. These can then be standardized by the standard deviation, which leaves a standardized index of abundance which keeps the anomalies on the same scale across different taxa.